
Isaac Asimov’s look at the world of 2014 – written in 1964.
The New York World’s Fair of 1964 is dedicated to “Peace Through Understanding.” Its glimpses of the world of tomorrow rule out thermonuclear warfare. And why not? If a thermonuclear war takes place, the future will not be worth discussing. So let the missiles slumber eternally on their pads and let us observe what may come in the nonatomized world of the future.
What is to come, through the fair’s eyes at least, is wonderful. The direction in which man is traveling is viewed with buoyant hope, nowhere more so than at the General Electric pavilion. There the audience whirls through four scenes, each populated by cheerful, lifelike dummies that move and talk with a facility that, inside of a minute and a half, convinces you they are alive.
The scenes, set in or about 1900, 1920, 1940 and 1960, show the advances of electrical appliances and the changes they are bringing to living. I enjoyed it hugely and only regretted that they had not carried the scenes into the future. What will life be like, say, in 2014 A.D., 50 years from now? What will the World’s Fair of 2014 be like?
I don’t know, but I can guess.
One thought that occurs to me is that men will continue to withdraw from nature in order to create an environment that will suit them better. By 2014, electroluminescent panels will be in common use. Ceilings and walls will glow softly, and in a variety of colors that will change at the touch of a push button.
Windows need be no more than an archaic touch, and even when present will be polarized to block out the harsh sunlight. The degree of opacity of the glass may even be made to alter automatically in accordance with the intensity of the light falling upon it.
There is an underground house at the fair which is a sign of the future. if its windows are not polarized, they can nevertheless alter the “scenery” by changes in lighting. Suburban houses underground, with easily controlled temperature, free from the vicissitudes of weather, with air cleaned and light controlled, should be fairly common. At the New York World’s Fair of 2014, General Motors’ “Futurama” may well display vistas of underground cities complete with light- forced vegetable gardens. The surface, G.M. will argue, will be given over to large-scale agriculture, grazing and parklands, with less space wasted on actual human occupancy.
Gadgetry will continue to relieve mankind of tedious jobs. Kitchen units will be devised that will prepare “automeals,” heating water and converting it to coffee; toasting bread; frying, poaching or scrambling eggs, grilling bacon, and so on. Breakfasts will be “ordered” the night before to be ready by a specified hour the next morning. Complete lunches and dinners, with the food semiprepared, will be stored in the freezer until ready for processing. I suspect, though, that even in 2014 it will still be advisable to have a small corner in the kitchen unit where the more individual meals can be prepared by hand, especially when company is coming.
Robots will neither be common nor very good in 2014, but they will be in existence. The I.B.M. exhibit at the present fair has no robots but it is dedicated to computers, which are shown in all their amazing complexity, notably in the task of translating Russian into English. If machines are that smart today, what may not be in the works 50 years hence? It will be such computers, much miniaturized, that will serve as the “brains” of robots. In fact, the I.B.M. building at the 2014 World’s Fair may have, as one of its prime exhibits, a robot housemaid*large, clumsy, slow- moving but capable of general picking-up, arranging, cleaning and manipulation of various appliances. It will undoubtedly amuse the fairgoers to scatter debris over the floor in order to see the robot lumberingly remove it and classify it into “throw away” and “set aside.” (Robots for gardening work will also have made their appearance.)
General Electric at the 2014 World’s Fair will be showing 3-D movies of its “Robot of the Future,” neat and streamlined, its cleaning appliances built in and performing all tasks briskly. (There will be a three-hour wait in line to see the film, for some things never change.)
The appliances of 2014 will have no electric cords, of course, for they will be powered by long- lived batteries running on radioisotopes. The isotopes will not be expensive for they will be by- products of the fission-power plants which, by 2014, will be supplying well over half the power needs of humanity. But once the isotype batteries are used up they will be disposed of only through authorized agents of the manufacturer.
And experimental fusion-power plant or two will already exist in 2014. (Even today, a small but genuine fusion explosion is demonstrated at frequent intervals in the G.E. exhibit at the 1964 fair.) Large solar-power stations will also be in operation in a number of desert and semi-desert areas — Arizona, the Negev, Kazakhstan. In the more crowded, but cloudy and smoggy areas, solar power will be less practical. An exhibit at the 2014 fair will show models of power stations in space, collecting sunlight by means of huge parabolic focusing devices and radiating the energy thus collected down to earth.
The world of 50 years hence will have shrunk further. At the 1964 fair, the G.M. exhibit depicts, among other things, “road-building factories” in the tropics and, closer to home, crowded highways along which long buses move on special central lanes. There is every likelihood that highways at least in the more advanced sections of the world*will have passed their peak in 2014; there will be increasing emphasis on transportation that makes the least possible contact with the surface. There will be aircraft, of course, but even ground travel will increasingly take to the air*a foot or two off the ground. Visitors to the 1964 fair can travel there in an “aquafoil,” which lifts itself on four stilts and skims over the water with a minimum of friction. This is surely a stop-gap. By 2014 the four stilts will have been replaced by four jets of compressed air so that the vehicle will make no contact with either liquid or solid surfaces.
Jets of compressed air will also lift land vehicles off the highways, which, among other things, will minimize paving problems. Smooth earth or level lawns will do as well as pavements. Bridges will also be of less importance, since cars will be capable of crossing water on their jets, though local ordinances will discourage the practice.
Much effort will be put into the designing of vehicles with “Robot-brains”*vehicles that can be set for particular destinations and that will then proceed there without interference by the slow reflexes of a human driver. I suspect one of the major attractions of the 2014 fair will be rides on small roboticized cars which will maneuver in crowds at the two-foot level, neatly and automatically avoiding each other.
For short-range travel, moving sidewalks (with benches on either side, standing room in the center) will be making their appearance in downtown sections. They will be raised above the traffic. Traffic will continue (on several levels in some places) only because all parking will be off-street and because at least 80 per cent of truck deliveries will be to certain fixed centers at the city’s rim. Compressed air tubes will carry goods and materials over local stretches, and the switching devices that will place specific shipments in specific destinations will be one of the city’s marvels.
Communications will become sight-sound and you will see as well as hear the person you telephone. The screen can be used not only to see the people you call but also for studying documents and photographs and reading passages from books. Synchronous satellites, hovering in space will make it possible for you to direct-dial any spot on earth, including the weather stations in Antarctica (shown in chill splendor as part of the ’64 General Motors exhibit).
For that matter, you will be able to reach someone at the moon colonies, concerning which General Motors puts on a display of impressive vehicles (in model form) with large soft tires*intended to negotiate the uneven terrain that may exist on our natural satellite.
Any number of simultaneous conversations between earth and moon can be handled by modulated laser beams, which are easy to manipulate in space. On earth, however, laser beams will have to be led through plastic pipes, to avoid material and atmospheric interference. Engineers will still be playing with that problem in 2014.
Conversations with the moon will be a trifle uncomfortable, but the way, in that 2.5 seconds must elapse between statement and answer (it takes light that long to make the round trip). Similar conversations with Mars will experience a 3.5-minute delay even when Mars is at its closest. However, by 2014, only unmanned ships will have landed on Mars, though a manned expedition will be in the works and in the 2014 Futurama will show a model of an elaborate Martian colony.
As for television, wall screens will have replaced the ordinary set; but transparent cubes will be making their appearance in which three-dimensional viewing will be possible. In fact, one popular exhibit at the 2014 World’s Fair will be such a 3-D TV, built life-size, in which ballet performances will be seen. The cube will slowly revolve for viewing from all angles.
One can go on indefinitely in this happy extrapolation, but all is not rosy.
As I stood in line waiting to get into the General Electric exhibit at the 1964 fair, I found myself staring at Equitable Life’s grim sign blinking out the population of the United States, with the number (over 191,000,000) increasing by 1 every 11 seconds. During the interval which I spent inside the G.E. pavilion, the American population had increased by nearly 300 and the world’s population by 6,000.
In 2014, there is every likelihood that the world population will be 6,500,000,000 and the population of the United States will be 350,000,000. Boston-to-Washington, the most crowded area of its size on the earth, will have become a single city with a population of over 40,000,000.
Population pressure will force increasing penetration of desert and polar areas. Most surprising and, in some ways, heartening, 2014 will see a good beginning made in the colonization of the continental shelves. Underwater housing will have its attractions to those who like water sports, and will undoubtedly encourage the more efficient exploitation of ocean resources, both food and mineral. General Motors shows, in its 1964 exhibit, the model of an underwater hotel of what might be called mouth-watering luxury. The 2014 World’s Fair will have exhibits showing cities in the deep sea with bathyscaphe liners carrying men and supplies across and into the abyss.
Ordinary agriculture will keep up with great difficulty and there will be “farms” turning to the more efficient micro-organisms. Processed yeast and algae products will be available in a variety of flavors. The 2014 fair will feature an Algae Bar at which “mock-turkey” and “pseudosteak” will be served. It won’t be bad at all (if you can dig up those premium prices), but there will be considerable psychological resistance to such an innovation.
Although technology will still keep up with population through 2014, it will be only through a supreme effort and with but partial success. Not all the world’s population will enjoy the gadgety world of the future to the full. A larger portion than today will be deprived and although they may be better off, materially, than today, they will be further behind when compared with the advanced portions of the world. They will have moved backward, relatively.
Nor can technology continue to match population growth if that remains unchecked. Consider Manhattan of 1964, which has a population density of 80,000 per square mile at night and of over 100,000 per square mile during the working day. If the whole earth, including the Sahara, the Himalayan Mountain peaks, Greenland, Antarctica and every square mile of the ocean bottom, to the deepest abyss, were as packed as Manhattan at noon, surely you would agree that no way to support such a population (let alone make it comfortable) was conceivable. In fact, support would fail long before the World-Manhattan was reached.
Well, the earth’s population is now about 3,000,000,000 and is doubling every 40 years. If this rate of doubling goes unchecked, then a World-Manhattan is coming in just 500 years. All earth will be a single choked Manhattan by A.D. 2450 and society will collapse long before that!
There are only two general ways of preventing this: (1) raise the death rate; (2) lower the birth rate. Undoubtedly, the world of A>D. 2014 will have agreed on the latter method. Indeed, the increasing use of mechanical devices to replace failing hearts and kidneys, and repair stiffening arteries and breaking nerves will have cut the death rate still further and have lifted the life expectancy in some parts of the world to age 85.
There will, therefore, be a worldwide propaganda drive in favor of birth control by rational and humane methods and, by 2014, it will undoubtedly have taken serious effect. The rate of increase of population will have slackened*but, I suspect, not sufficiently.
One of the more serious exhibits at the 2014 World’s Fair, accordingly, will be a series of lectures, movies and documentary material at the World Population Control Center (adults only; special showings for teen-agers).
The situation will have been made the more serious by the advances of automation. The world of A.D. 2014 will have few routine jobs that cannot be done better by some machine than by any human being. Mankind will therefore have become largely a race of machine tenders. Schools will have to be oriented in this direction. Part of the General Electric exhibit today consists of a school of the future in which such present realities as closed-circuit TV and programmed tapes aid the teaching process. It is not only the techniques of teaching that will advance, however, but also the subject matter that will change. All the high-school students will be taught the fundamentals of computer technology will become proficient in binary arithmetic and will be trained to perfection in the use of the computer languages that will have developed out of those like the contemporary “Fortran” (from “formula translation”).
Even so, mankind will suffer badly from the disease of boredom, a disease spreading more widely each year and growing in intensity. This will have serious mental, emotional and sociological consequences, and I dare say that psychiatry will be far and away the most important medical specialty in 2014. The lucky few who can be involved in creative work of any sort will be the true elite of mankind, for they alone will do more than serve a machine.
Indeed, the most somber speculation I can make about A.D. 2014 is that in a society of enforced leisure, the most glorious single word in the vocabulary will have become work!
https://www.nytimes.com/books/97/03/23/lifetimes/asi-v-fair.html


 Flexible Displays
Flexible Displays 3-D Holograms
3-D Holograms Identity-Detecting Advertisement Cameras
Identity-Detecting Advertisement Cameras
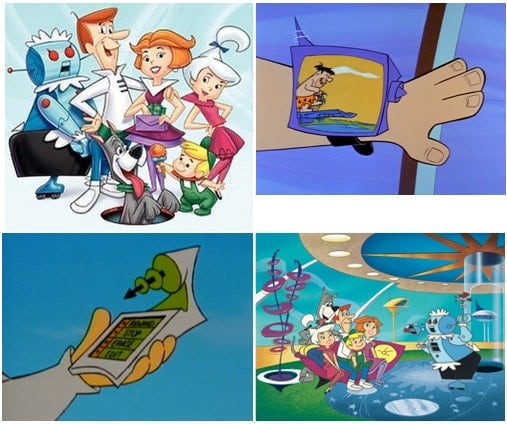












 Is prediction the way to invent the future? For the portable TV it was certainly the case.
Is prediction the way to invent the future? For the portable TV it was certainly the case.