Introduction
Communication technology has come to be considered as an essential service, with mobile communication playing a pivotal role in the advancement of technology and the human race.
This has resulted in researchers, governments and private operators investing in research for the continuous advancement of the mobile communications technology. Mobile communications generations commenced with voice-only systems and migrated to a generation with data as an add-on. This technology advanced to generations where data and voice competed for dominance – and now data transmission (Internet Protocol) is the current driver for the 5G mobile communications technology.
The advancement of the mobile communications standard is driven by a complex mix of new applications, technologies and user demand. In this era of artificial intelligence coupled with data science and very high but low-cost cloud applications and embedded sensors, there is a need for a communications standard that can harmonize all these applications and enable the users to extract the benefits associated with the new technologies.
5G technology is sadly a victim of both global politics and an opportunistic conspiracy as its deployment coincided with the spread of the Covid-19 global pandemic, thus making it easy for the conspiracy theorist to associate 5G with the spread of corona virus. The success of this conspiracy is such that even countries without any 5G deployment have seen cases of attacks on existing communication infrastructure, with several public figures and opinion leaders contributing to the spread of the conspiracy by relying on sentiments and untruths to support their theories. While this has caused a lot of damage to the infrastructure of the operators, it has also showed that there is a need for a robust change management system before new technologies with mass public applications are deployed.
This article is an attempt to debunk some of these conspiracy theories by showcasing the technical specifications of the technology and decoupling the 5G communications technology from the corona virus spread.
Frequency spectrum for mobile communication
One of the most significant considerations for wireless transmissions is the amount of attenuation the transmission will be exposed to as the signal travels through the atmosphere. Figure 1 shows the attenuation of several portions of the spectrum as the signal is transmitted through the atmosphere. Attenuation due to water and oxygen are lowest at sub 10GHz while between 60- 100GHz, the oxygen attenuation rises significantly. This means that while the higher frequencies have more bandwidths, they are exposed to very high amounts of attenuation. This is why these frequencies have not been used for mobile communication. However, the increasing rise in data intensive applications has led to the consideration of frequencies beyond 10GHz with selected pockets around 24GHz – 29GHz and 37GHz -43GHz and higher bands for 5G deployments.
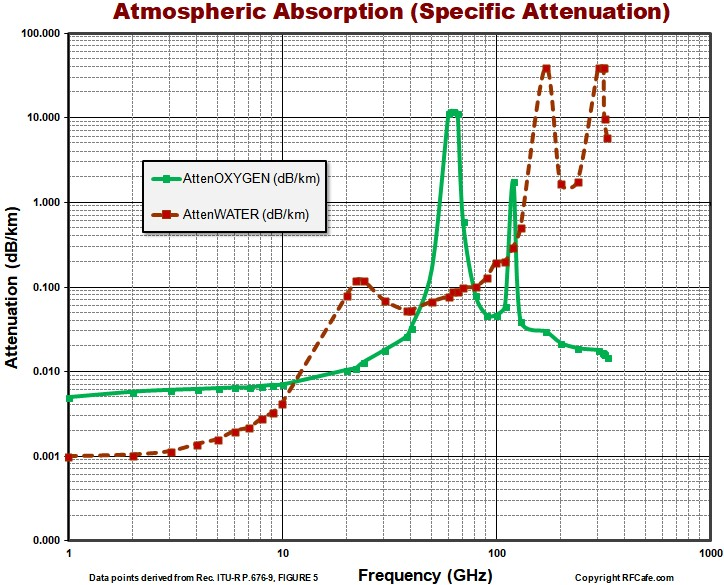
Figure 1. Atmospheric Absorption of signals
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum shown in figure 2 comprises of signals of different characteristics. These characteristics determine their range of applications. While some can be harmful to humans, others are safe for use around humans. The safety of human life is the most significant criterion for application of these frequencies and there are several agencies and tests required to ensure that technologies are within the safe operational region with all the associated margins adhered to. The EMF spectrum comprise a range of spectrum with frequencies capable of generating ionizing radiation (ionizing radiations are radiations with enough energy such that during an interaction with an atom, it can remove tightly bound electrons from the orbit of an atom, causing the atom to become charged or ionized). The portions of the spectrum with ionizing radiations are not allocated for communication service due to the harmful effects of signals at this frequency.
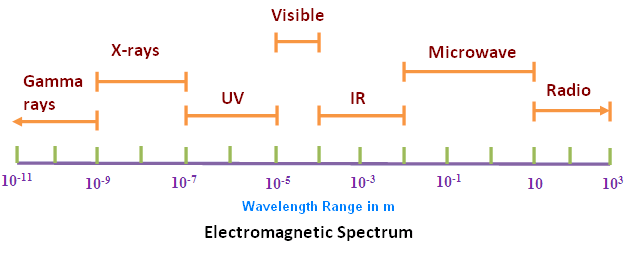
Figure 2. Electromagnetic spectrum
Communication Spectrum of the EMF
The portion of the EMF utilized for communication is the radio and microwave bands which range from 3Hz to 300GHz. This spectrum shown in Figure 3 is well outside the range of the ionizing frequency spectrum which ranges from 3PHz to 300EHz.

Figure 3. EMF spectrum showing key applications and the ionizing band
5G Deployments
Current 5G deployments are either at sub 2GHz, sub 6GHz or above 6GHz frequency bands. This wide array of spectrum and the associated differences in the levels of attenuation places a demand for a multi-application scenario for the deployment of 5G. The most promising approach and the easiest approach has been to deploy voice services at sub 2GHz, which is why so much work has been undertaken to refarm some TV spectrum and older telecom spectrum. This approach will enable operators to utilize existing cell sites with minimal infrastructure changes, while the design of the mobile phones will not require significant modifications as existing chipsets can still be used in equipment design since the frequencies are within the range of current multiband phones.
For deployments at higher frequencies (above 6GHz), the operators will first of all have to pay for the spectrum and will be exposed to much higher infrastructure costs, as the higher frequencies mean smaller coverage areas, thus many more cell sites would be required to provide the necessary coverage. Users would also have to change phones as our current phones are designed for specific sub 6GHz frequency bands and modulation schemes. None of these have happened yet as very few countries have deployed 5G at these higher frequencies.
5G use cases
The applications or use cases for 5G will be determined by the frequency around which the 5G is deployed in each given area. The availability of frequency for 5G both in the sub 2GHz, sub 6GHz band and the above 6GHz band creates a deployment with very different characteristics. This is determined by the fact that while the bandwidth at the sub 2GHz band is much lower than the bandwidth at the above 6GHz band by the order of several GHz, the attenuation faced by the above 6GHz band is several magnitudes higher than the attenuation faced by the sub 6GHz band and especially the sub 2GHz band. The different uses cases can be grouped as shown in figure 4.
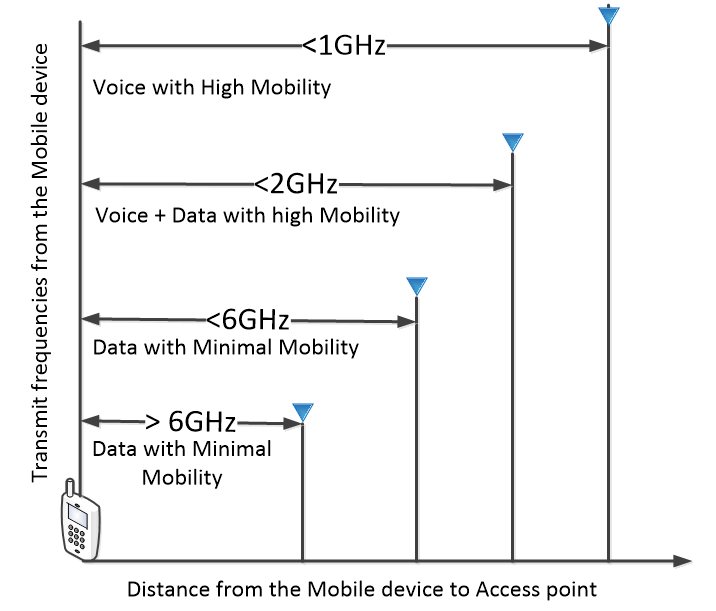
Figure 4. Typical 5G use cases determined by coverage range
This multi-application capability of the 5G spectrum shows that for the deployment of the service at all the proposed frequencies, the mobile phones must be able to handle a wide range of frequencies. This will place a lot of strain on the communication infrastructure design.
To ease mobile phone device applications, the approach for the deployment of 5G for voice is primarily restricted to the sub 2GHz band with the use of refarmed frequencies from TV white spaces and older telecom standards at 700MHz band. This approach allows the operators to utilize existing cell sites and infrastructure with minimal modification. The deployments above 6GHz are reserved for applications such as the IoT and other data driven application like virtual reality, self-driving cars and a host of other artificial intelligence-driven applications with 5G deployment providing the communication infrastructure.
The 5G use cases are also classified under the following categories:
- Fixed Wireless Access. This is to provide high speed internet access to homes using wireless networks such as the millimetre waves.
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband. This is a service that promises faster cloud connected services. It promises to provide cloud computing with higher date rates and lower latency and lower cost per bit. This also promises an all ways- on, always connected, high speed internet access with real time responsiveness in high mobility scenarios. This will support augmented and virtual reality applications.
- Machine to Machine type communications. This use case is one of the most anticipated applications of 5G. This is fuelled by the increasing numbers of embedded sensors and the IoT platform coupled with data analytics and artificial intelligence tools. It is estimated that potential IoT sensors will exceed 20 billion by the end of the year.
- Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communications. This use case focuses on the increased reliability pf industrial automation systems by providing ultra reliable low latency links. Typical applications include self-driving cars, smart grid control and industrial automation, robotics and drone control and coordination
- 6G applications. The 6G standard will focus on the development of applications which will ride on the 5G communications network infrastructure. These applications will leverage on IoT, artificial intelligence, data analytics and virtual reality technologies to develop novel solutions both for personal and industrial applications
5G Radiation and COVID-19 spread
The claims of 5G radiation being responsible for COVID has been disputed on the grounds that the spectrum does not generate any ionizing radiation. It has also been disproved on the grounds that the energy per photon of the frequency is much lower than that of the ionization radiation band. In terms of transmit power, if the transmit power of the BTS is increased tremendously to overcome the path loss and increase the coverage area of the cells, there will also be a corresponding need for the increase in the transmit power of the mobile phones to ensure a bidirectional scheme is achieved. This will require a return to the era of bulky and heavy phones as the transmit power relies heavily on battery power. All the recently released 5G phones are designed to comply with the specified electromagnetic compatibility and radiation settings, as such the radiation is within the safe limits. This limitation on the transmit power of the new phones coupled with the use of existing sub 2GHz for the recently deployed 5G networks provides sufficient proof that 5G has no connection with the spread of coronavirus in any way.
Given the current deployment characteristic of 5G and all the frequencies for all the possible use cases both for the near future and the far future into the 6th Generation era, the fact that the frequencies are in the non-ionizing band coupled with all the stringent regulations makes it very unlikely that a mobile communication technology either at 5G or 6G will place either the immediate users or communities at a health risk.







